Greenhouse & Indoor Growing
Extend your growing season or grow year-round with greenhouses and indoor setups. Learn about structure types, grow lights, climate control, and best crops for controlled environments.
Greenhouse Types
Choose the right structure based on your climate, budget, and growing goals.
Best for: Hardening off, extending season, cold-hardy greens
Pros
- Very affordable
- No power needed
- Easy to build DIY
- Portable
Cons
- Limited space
- No climate control
- Manual venting needed
Best for: Season extension, frost protection, market gardens
Pros
- Affordable per sq ft
- Good for large areas
- Extends season 4-6 weeks
- Simple construction
Cons
- Less insulation
- Plastic degrades (4-6 years)
- Can overheat
Best for: Attached growing, easy access, year-round in mild climates
Pros
- Shares house heat
- Convenient access
- Can use house electric
- Foundation already exists
Cons
- Limited sunlight angles
- Takes yard space
- Can add humidity to house
Best for: Year-round growing, tropical plants, serious hobbyists
Pros
- Maximum light
- Best insulation
- Long lasting
- Beautiful aesthetic
Cons
- Expensive
- Requires foundation
- Heating costs
- Professional install often needed
Greenhouse Climate Control
- Most vegetables prefer 10°F cooler at night
- Tomatoes need night temps above 55°F to set fruit
- Use thermostat-controlled heaters
- Open vents when temps exceed 85°F
- Too high = fungal diseases
- Too low = spider mites thrive
- Use humidity trays or humidifiers
- Good ventilation prevents problems
- Prevents fungal diseases
- Strengthens plant stems
- Use oscillating fans on low
- Open vents when possible
- Plants use CO2 for photosynthesis
- Outdoor air is ~400 ppm
- Closed spaces can deplete CO2
- Ventilation usually sufficient
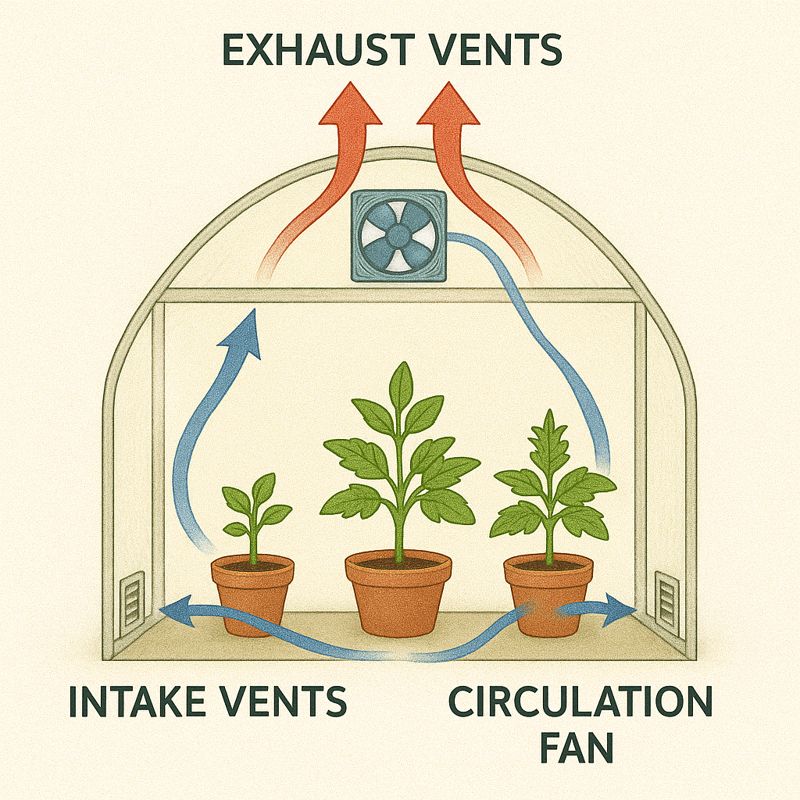
Proper ventilation creates air circulation that regulates temperature, humidity, and prevents disease
Seasonal Greenhouse Management
- Open all vents and doors daily
- Use shade cloth (30-50%) if over 90°F
- Water early morning
- Run exhaust fans
- Whitewash glass to reduce heat
- Seal gaps and add insulation
- Use thermal mass (water barrels)
- Add row covers inside for extra protection
- Ventilate midday on sunny days
- Use heating mats for seedlings
Transitioning Plants: Hardening Off
Plants started indoors or in greenhouses need gradual exposure to outdoor conditions before transplanting. This process, called "hardening off," helps them adapt to stronger sunlight, wind, and temperature fluctuations.
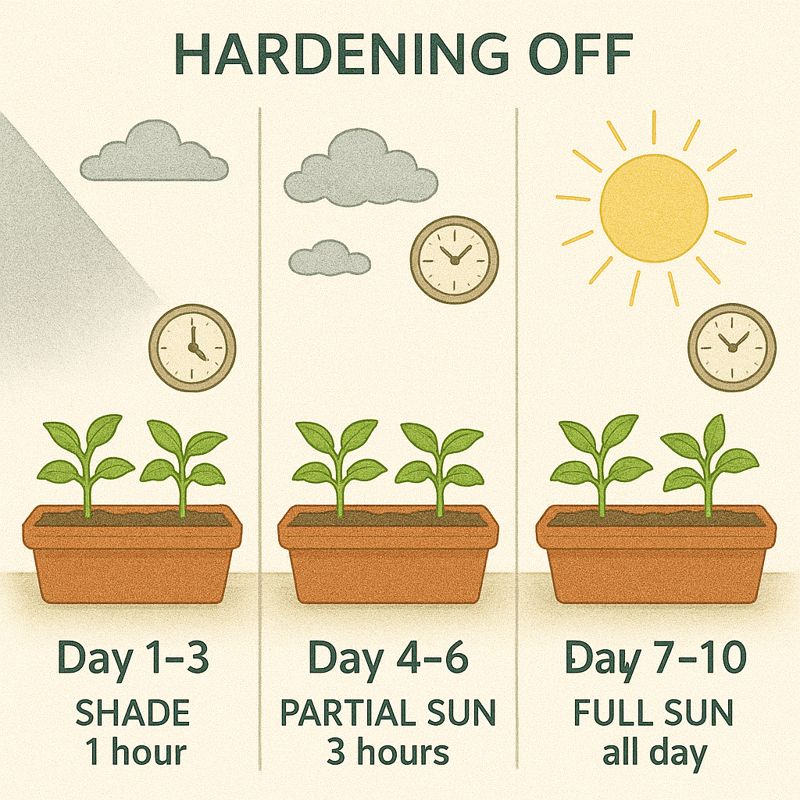
Gradually acclimate plants over 7-10 days to prevent shock and transplant failure
Week 1 (Days 1-3)
- - Start with 1-2 hours in shade
- - Bring inside at night
- - Protect from wind
- - Monitor closely for wilting
Week 2 (Days 4-10)
- - Increase sun exposure daily
- - Extend outdoor time gradually
- - Leave out overnight after Day 7
- - Ready to transplant by Day 10